Routing Protocols
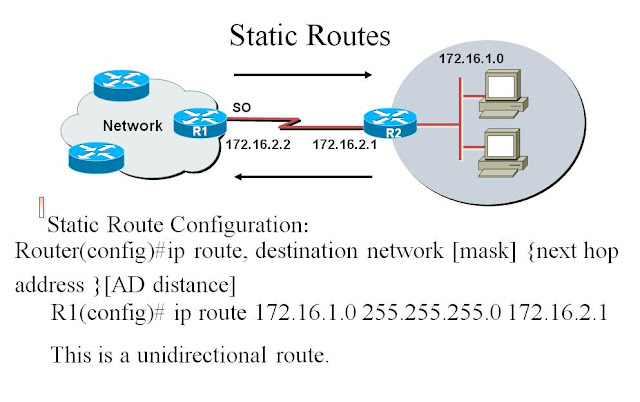
ROUTING BASICS The term routing is used for taking a packet from one device and sending it through the network to another device on a different network For routing a router must know following things Ø Destination address Ø Neighbour routers from which it can learn about remote networks, Possible routes to all remote networks Ø The best route to each remote network Ø How to maintain and verify routing information Ø They are the set of rules used by a router when it communicates routing information between neighboring router Ø Routing protocols use metrics to evaluate what path will be the best for a packet to travel Ø A metric is a standard of measurements; such as path bandwidth, reliability, delay, current load on that path etc; i.e used by routing algorithms to determine the optimal path to a destination. Desirable properties of a router • Correctness and simplicity: The packets are to be correctly delivered. Simpler the routing algorithm, it is bette